Encrypting data on portable devices
Many users use portable devices (such as USB hard drives or USB memory sticks) to store research data, whether this is to allow the data to be portable or serve as an additional backup device.
One of the major risks with using these portable devices is that if the device is ever lost, stolen or borrowed, it is easy to access to any research data that is stored on the device. Obviously some data might be considered “open” and happily shared around, but if the data is confidential in nature, containing ethic information or holds valuable intellectual property, then is it critical that this data is securely stored so that if it ever got into the wrong hands, the data cannot be easily accessed.
To secure data on portable devices, it is recommend to encrypt the devices using a data encryption tool.
It should be noted that when using any type of data encryption, it is critical that you use a hard to “guess” password. Secondly, you will need to ensure that the password you are using is remembered and stored in a safe place (storing it on a sticky note on the device really defeats the purpose of using encryption)! Unlike user accounts and many other web systems, if the password is forgotten, there is no process to change or retrieve the password. In the event that the password cannot be remembered, consider the data stored within the encrypted device lost forever.
The following information provides instructions on data encryption which can be enabled on portable devices.
USING MICROSOFT’S BITLOCKER TO ENCRYPTED A PORTABLE DEVICE (WINDOWS COMPUTERS ONLY)
Before getting started it is important to note the following
- Microsoft BitLocker is proprietary software and will only work on Microsoft Windows computers – therefore the encrypted data will not be able to be accessed from an Apple Mac or Linux Computer. If you wish to use the portable device on different platforms, this method is not suitable for this purpose.
- Microsoft BitLocker is only available for select editions, available on Pro, Enterprise and Education versions of Windows 10 and 11. This means it is not available on the Home edition of Windows 10/11. BitLocker should be available on all CQUniversity Windows computers but if you encrypt your data with a CQU machine and then attempt to access that data on a personal computer that doesn’t support Bitlocker, you will not be able to access the encrypted data. It should also be noted that you cannot download this software to make it work on the other versions of the operating systems. This can only be achieved by upgrading Windows to a higher version which will come at a cost.
- If you need to access your data across multiple machines or on a machine that isn’t listed above, we recommend performing a test with a memory device that doesn’t have valuable data stored on it to ensure it works across the platforms required, before encrypting your valuable data.
Encrypting portable device using BitLocker instructions
(These instructions were written for Windows 7, Windows 10/11 instructions can be found here)
- Go to Control Panel and open “BitLocker Drive Encryption
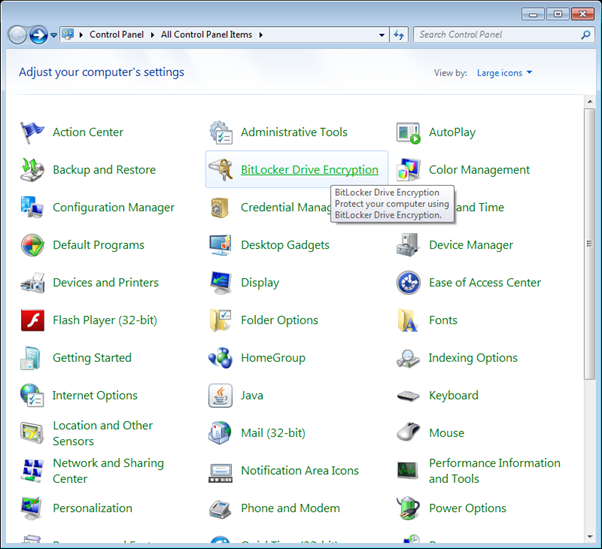
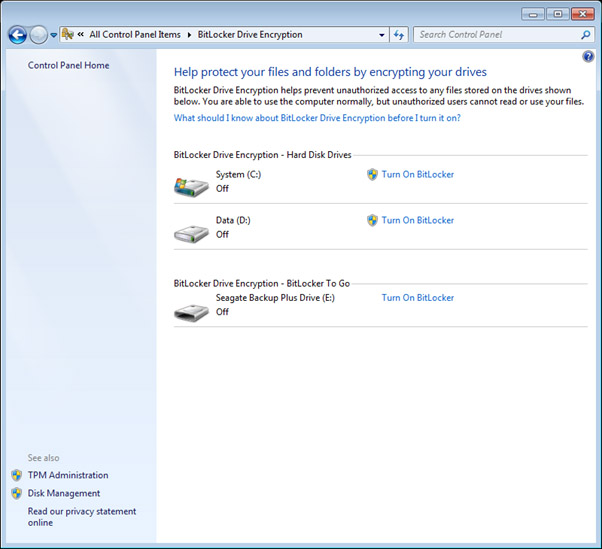
- Select the device you wish to encrypt select the “Turn On BitLocker” on the device you wish to encrypt. In the example image below, the Seagate device was selected.
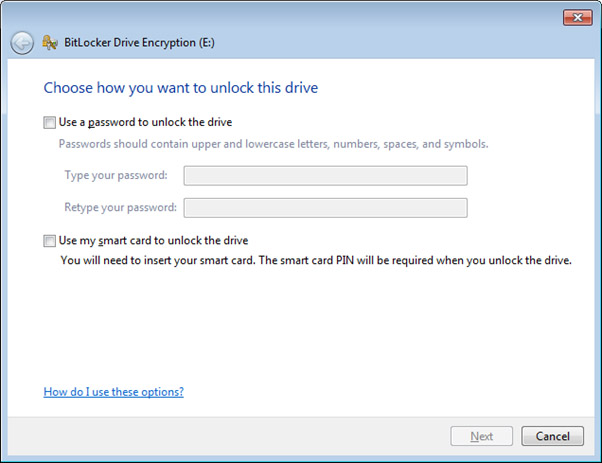
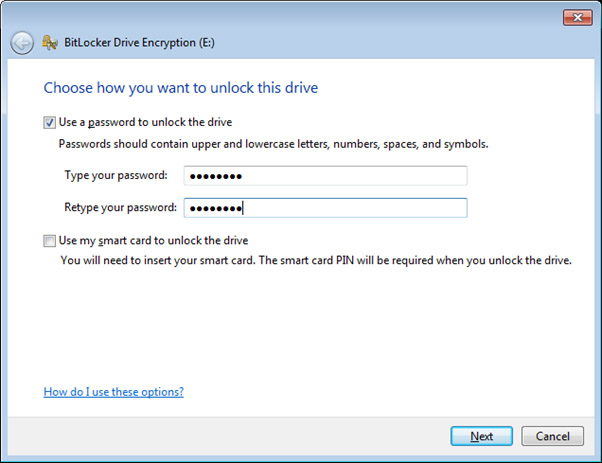
- The simplest method is to “Password protect” a device. Simply select the “Use a password to unlock the drive” and enter a Password. It is critical that you use a hard to “guess” password.
- Ensure that the password you are using is remembered and stored in a safe place (storing it on a sticky note on the device really defeats the purpose of using encryption)! Unlike user accounts and many other web systems, if the password is forgotten, there is no process to change or retrieve the password. In the event that the password cannot be remembered, consider the data stored within the encrypted device lost forever.
- Once a password is entered, there is the option to save the recovery key to a file or print the recovery. Obviously these details need to be saved in a secure location, otherwise this information can be easily used to unlock the encrypted data.
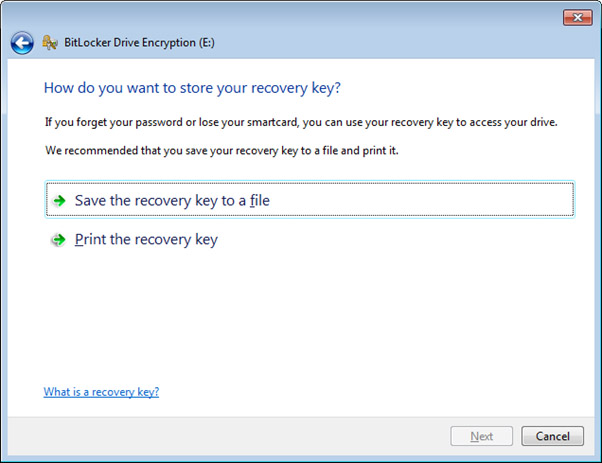
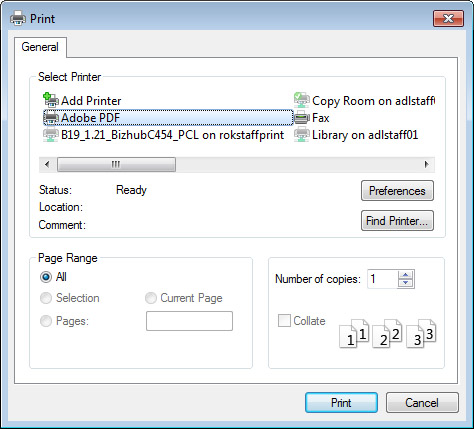
- An option to keep a record of this recovery key is to print the key as a PDF document. But again, keep this in a safe and secure place.
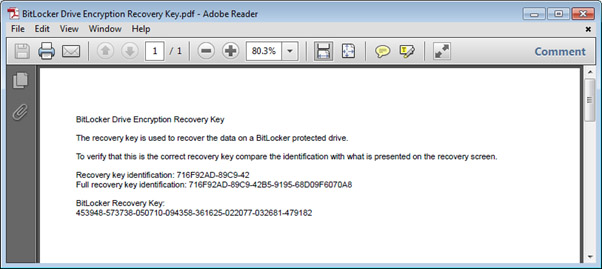
- An example of the Recovery Key can be seen in the image below.
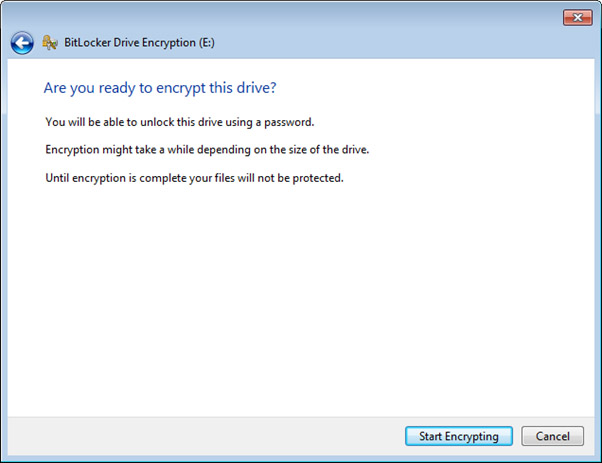
- Once you are ready to encrypt the drive, select the “Start Encrypting” button to proceed. It should be noted that depending on the size of the drive, this process can take quite a while. For example, it took 3.5 hours to encrypt a 1TB drive using a laptop.
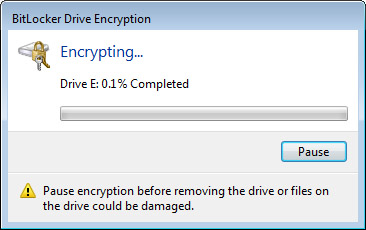
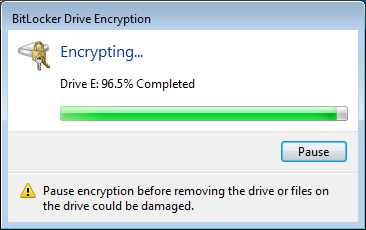
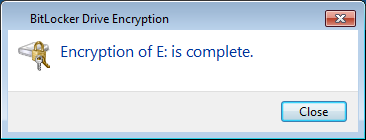
Accessing a portable device using BitLocker
- Simply connect the portable device into a windows computer (running one of the select editions (Ultimate and Enterprise) of Windows Vista and later). Once you try to access the device (E: in the example image below), you will be then be asked to enter the password to unlock the device.
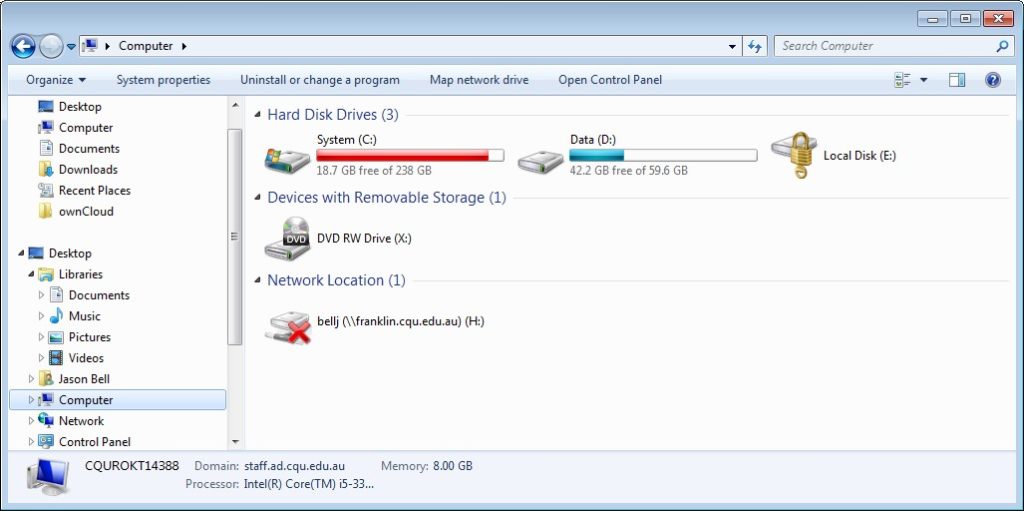
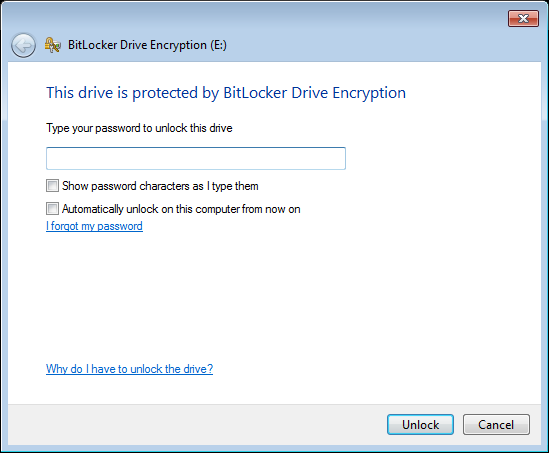
- Once the device is unlocked, you can then use it like a normal “unencrypted device”.
Managing an encrypted (BitLocker) device
- Once the device is unlocked, you can manage some BitLocker options by right clicking on the device and selecting the “Manage BitLocker…” option.
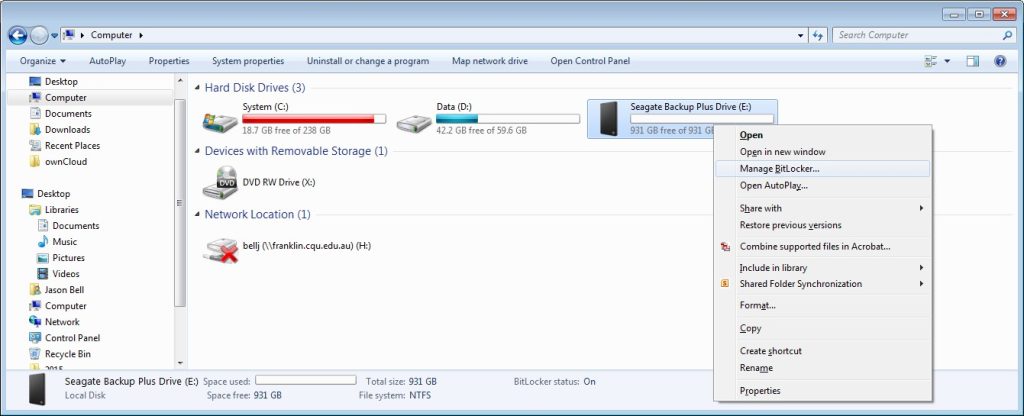
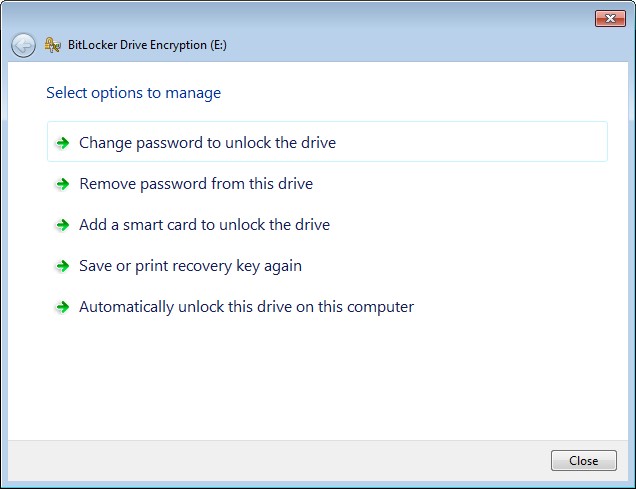
- This allows you to change the password, remove the password and a variety of other options.
Additional information on BitLocker
- https://support.microsoft.com/en-us/windows/device-encryption-in-windows-ad5dcf4b-dbe0-2331-228f-7925c2a3012d – BitLocker guide for Windows 10/11
- http://windows.microsoft.com/en-au/windows-vista/bitlocker-drive-encryption-overview – BitLocker Drive Encryption Overview
- https://technet.microsoft.com/en-gb/library/ee424323.aspx – Scenario 2: Turning On BitLocker Drive Encryption on a Fixed or Removable Data Drive (Windows 7)
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/BitLocker – BitLocker Wikipedia
- http://www.howtogeek.com/192894/how-to-set-up-bitlocker-encryption-on-windows – How to Set Up BitLocker Encryption on Windows
- http://blogs.technet.com/b/uspartner_ts2team/archive/2010/03/17/what-is-bitlocker-what-does-it-do-what-does-it-not-do.aspx – What is BitLocker? What does it do? What does it not do?

